[Beta] Memory
Many LLM applications have a conversational interface. An essential component of a conversation is being able to refer to information introduced earlier in the conversation. At bare minimum, a conversational system should be able to access some window of past messages directly. A more complex system will need to have a world model that it is constantly updating, which allows it to do things like maintain information about entities and their relationships.
We call this ability to store information about past interactions "memory". LangChain provides utilities for adding memory to a system. These utilities can be used by themselves or incorporated seamlessly into a chain.
Most memory-related functionality in LangChain is marked as beta. This is for two reasons:
- Most functionality (with some exceptions, see below) is not production ready.
- Most functionality (with some exceptions, see below) works with Legacy chains, not the newer LCEL syntax.
The main exception to this is the ChatMessageHistory functionality. This functionality is largely production ready and does integrate with LCEL.
- LCEL Runnables: See these docs for an overview of how to use ChatMessageHistory with LCEL runnables.
- Integrations: See these docs for an introduction to the various ChatMessageHistory integrations.
Introduction
A memory system needs to support two basic actions: reading and writing. Recall that every chain defines some core execution logic that expects certain inputs. Some of these inputs come directly from the user, but some of these inputs can come from memory. A chain will interact with its memory system twice in a given run.
- AFTER receiving the initial user inputs but BEFORE executing the core logic, a chain will READ from its memory system and augment the user inputs.
- AFTER executing the core logic but BEFORE returning the answer, a chain will WRITE the inputs and outputs of the current run to memory, so that they can be referred to in future runs.
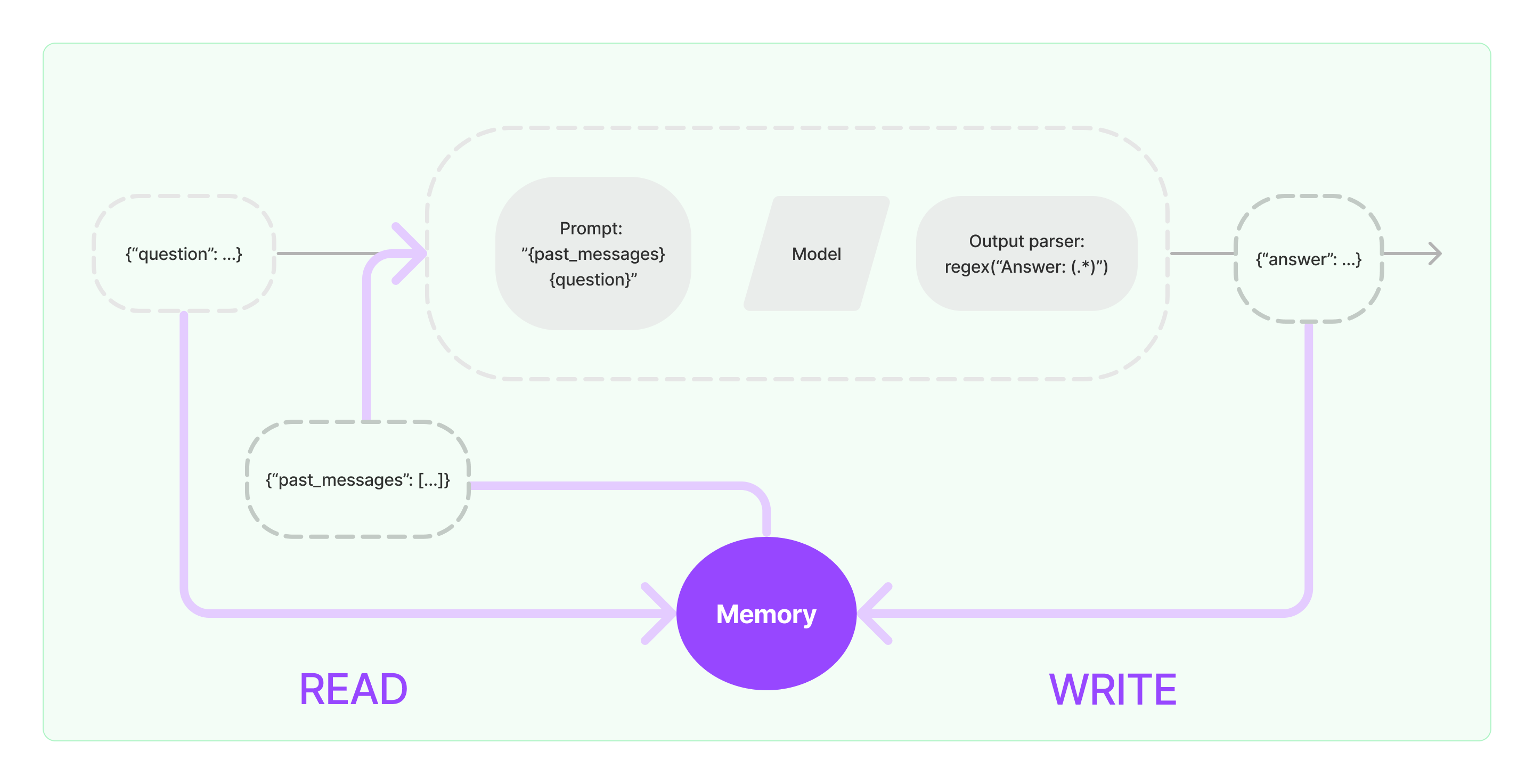
Building memory into a system
The two core design decisions in any memory system are:
- How state is stored
- How state is queried
Storing: List of chat messages
Underlying any memory is a history of all chat interactions. Even if these are not all used directly, they need to be stored in some form. One of the key parts of the LangChain memory module is a series of integrations for storing these chat messages, from in-memory lists to persistent databases.
- Chat message storage: How to work with Chat Messages, and the various integrations offered.
Querying: Data structures and algorithms on top of chat messages
Keeping a list of chat messages is fairly straight-forward. What is less straight-forward are the data structures and algorithms built on top of chat messages that serve a view of those messages that is most useful.
A very simple memory system might just return the most recent messages each run. A slightly more complex memory system might return a succinct summary of the past K messages. An even more sophisticated system might extract entities from stored messages and only return information about entities referenced in the current run.
Each application can have different requirements for how memory is queried. The memory module should make it easy to both get started with simple memory systems and write your own custom systems if needed.
- Memory types: The various data structures and algorithms that make up the memory types LangChain supports
Get started
Let's take a look at what Memory actually looks like in LangChain. Here we'll cover the basics of interacting with an arbitrary memory class.
Let's take a look at how to use BufferMemory in chains. BufferMemory is an extremely simple form of memory that just keeps a list of chat messages in a buffer and passes those into the prompt template:
import { BufferMemory } from "langchain/memory";
import { HumanMessage, AIMessage } from "@langchain/core/messages";
const memory = new BufferMemory();
await memory.chatHistory.addMessage(new HumanMessage("Hi!"));
await memory.chatHistory.addMessage(new AIMessage("What's up?"));
When using memory in a chain, there are a few key concepts to understand. Note that here we cover general concepts that are useful for most types of memory. Each individual memory type may have its own parameters and concepts.
What variables get returned from memory
Before going into the chain, various variables are read from memory. These have specific names which need to align with the variables the chain expects.
You can see what these variables are by calling await memory.loadMemoryVariables({}).
Note that the empty dictionary that we pass in is just a placeholder for real variables.
If the memory type you are using is dependent upon the input variables, you may need to pass values here.
await memory.loadMemoryVariables({});
// { history: "Human: Hi!\AI: What's up?" }
In this case, you can see that loadMemoryVariables returns a single key, history.
This means that your chain (and likely your prompt) should expect an input named history.
You can generally control this variable through parameters on the memory class. For example, if you want the
memory variables to be returned under the key chat_history you can do:
const memory2 = new BufferMemory({
memoryKey: "chat_history",
});
await memory2.chatHistory.addMessage(new HumanMessage("Hi!"));
await memory2.chatHistory.addMessage(new AIMessage("What's up?"));
await memory2.loadMemoryVariables({});
// { chat_history: "Human: Hi!\AI: What's up?" }
The parameter name to control these keys may vary per memory type, but it's important to understand that (1) this is controllable, and (2) how to control it.
Whether memory is a string or a list of messages
One of the most common types of memory involves returning a list of chat messages. These can either be returned as a single string, all concatenated together (useful when they will be passed into LLMs) or a list of ChatMessages (useful when passed into ChatModels).
By default, they are returned as a single string. In order to return as a list of messages, you can set returnMessages to true.
const messageMemory = new BufferMemory({
returnMessages: true,
});
await messageMemory.chatHistory.addMessage(new HumanMessage("Hi!"));
await messageMemory.chatHistory.addMessage(new AIMessage("What's up?"));
await messageMemory.loadMemoryVariables({});
/*
{
history: [
HumanMessage {
content: 'Hi!',
additional_kwargs: {}
},
AIMessage {
content: "What's up?",
additional_kwargs: {}
}
]
}
*/
What keys are saved to memory
Often times chains take in or return multiple input/output keys. In these cases, how can we know
which keys we want to save to the chat message history? This is generally controllable by inputKey and outputKey
parameters on the memory types. These default to None - and if there is only one input/output key the class
will default to just use that key. However, if there are multiple input/output keys then you MUST specify the name of
which one to use.
End to end example
Finally, let's take a look at using this in a chain. We'll use an LLMChain, and show working with both an LLM and a ChatModel.
Using an LLM
import { OpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { PromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts";
import { LLMChain } from "langchain/chains";
const llm = new OpenAI({ temperature: 0 });
// Notice that a "chat_history" variable is present in the prompt template
const template = `You are a nice chatbot having a conversation with a human.
Previous conversation:
{chat_history}
New human question: {question}
Response:`;
const prompt = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate(template);
// Notice that we need to align the `memoryKey` with the variable in the prompt
const llmMemory = new BufferMemory({ memoryKey: "chat_history" });
const conversationChain = new LLMChain({
llm,
prompt,
verbose: true,
memory: llmMemory,
});
// Notice that we just pass in the `question` variable.
// `chat_history` gets populated by the memory class
await conversationChain.invoke({ question: "What is your name?" });
await conversationChain.invoke({ question: "What did I just ask you?" });
// { text: ' My name is OpenAI. What is your name?' }
// { text: ' You just asked me what my name is.' }
Using a chat model
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import {
ChatPromptTemplate,
MessagesPlaceholder,
} from "@langchain/core/prompts";
const chatModel = new ChatOpenAI({ temperature: 0 });
const chatPrompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromMessages([
["system", "You are a nice chatbot having a conversation with a human."],
// The variable name here is what must align with memory
new MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
["human", "{question}"],
]);
// Notice that we set `returnMessages: true` to return raw chat messages that are inserted
// into the MessagesPlaceholder.
// Additionally, note that `"chat_history"` aligns with the MessagesPlaceholder name.
const chatPromptMemory = new BufferMemory({
memoryKey: "chat_history",
returnMessages: true,
});
const chatConversationChain = new LLMChain({
llm: chatModel,
prompt: chatPrompt,
verbose: true,
memory: chatPromptMemory,
});
// Notice that we just pass in the `question` variables - `chat_history` gets populated by memory
await chatConversationChain.invoke({ question: "What is your name?" });
await chatConversationChain.invoke({ question: "What did I just ask you?" });
// { text: "Hello! I'm an AI chatbot, so I don't have a personal name. You can just call me Chatbot. How can I assist you today?" }
// { text: 'You just asked me what my name is.' }
Next steps
And that's it for getting started! Please see the other sections for walkthroughs of more advanced topics.