Retrieval augmented generation (rag)
Overview
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful technique that enhances language models by combining them with external knowledge bases. RAG addresses a key limitation of models: models rely on fixed training datasets, which can lead to outdated or incomplete information. When given a query, RAG systems first search a knowledge base for relevant information. The system then incorporates this retrieved information into the model's prompt. The model uses the provided context to generate a response to the query. By bridging the gap between vast language models and dynamic, targeted information retrieval, RAG is a powerful technique for building more capable and reliable AI systems.
Key concepts
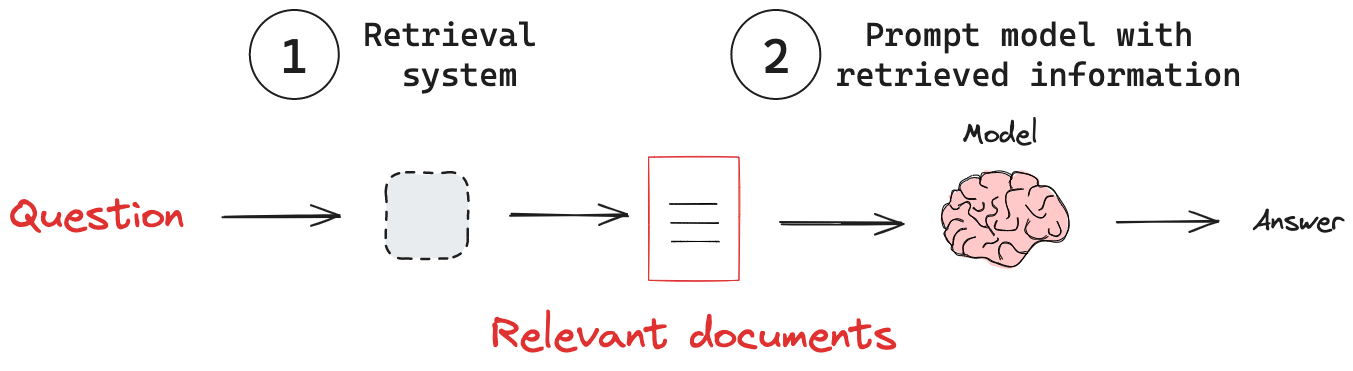
(1) Retrieval system: Retrieve relevant information from a knowledge base.
(2) Adding external knowledge: Pass retrieved information to a model.
Retrieval system
Model's have internal knowledge that is often fixed, or at least not updated frequently due to the high cost of training. This limits their ability to answer questions about current events, or to provide specific domain knowledge. To address this, there are various knowledge injection techniques like fine-tuning or continued pre-training. Both are costly and often poorly suited for factual retrieval. Using a retrieval system offers several advantages:
- Up-to-date information: RAG can access and utilize the latest data, keeping responses current.
- Domain-specific expertise: With domain-specific knowledge bases, RAG can provide answers in specific domains.
- Reduced hallucination: Grounding responses in retrieved facts helps minimize false or invented information.
- Cost-effective knowledge integration: RAG offers a more efficient alternative to expensive model fine-tuning.
See our conceptual guide on retrieval.
Adding external knowledge
With a retrieval system in place, we need to pass knowledge from this system to the model. A RAG pipeline typically achieves this following these steps:
- Receive an input query.
- Use the retrieval system to search for relevant information based on the query.
- Incorporate the retrieved information into the prompt sent to the LLM.
- Generate a response that leverages the retrieved context.
As an example, here's a simple RAG workflow that passes information from a retriever to a chat model:
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
// Define a system prompt that tells the model how to use the retrieved context
const systemPrompt = `You are an assistant for question-answering tasks.
Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer the question.
If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know.
Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise.
Context: {context}:`;
// Define a question
const question =
"What are the main components of an LLM-powered autonomous agent system?";
// Retrieve relevant documents
const docs = await retriever.invoke(question);
// Combine the documents into a single string
const docsText = docs.map((d) => d.pageContent).join("");
// Populate the system prompt with the retrieved context
const systemPromptFmt = systemPrompt.replace("{context}", docsText);
// Create a model
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
temperature: 0,
});
// Generate a response
const questions = await model.invoke([
{
role: "system",
content: systemPromptFmt,
},
{
role: "user",
content: question,
},
]);
RAG a deep area with many possible optimization and design choices:
- See this excellent blog from Cameron Wolfe for a comprehensive overview and history of RAG.
- See our RAG how-to guides.
- See our RAG tutorials.
- See our RAG from Scratch course, with code and video playlist.
- Also, see our RAG from Scratch course on Freecodecamp.