Build a Question Answering application over a Graph Database
In this guide we’ll go over the basic ways to create a Q&A chain over a graph database. These systems will allow us to ask a question about the data in a graph database and get back a natural language answer.
⚠️ Security note ⚠️
Building Q&A systems of graph databases requires executing model-generated graph queries. There are inherent risks in doing this. Make sure that your database connection permissions are always scoped as narrowly as possible for your chain/agent’s needs. This will mitigate though not eliminate the risks of building a model-driven system. For more on general security best practices, see here.
Architecture
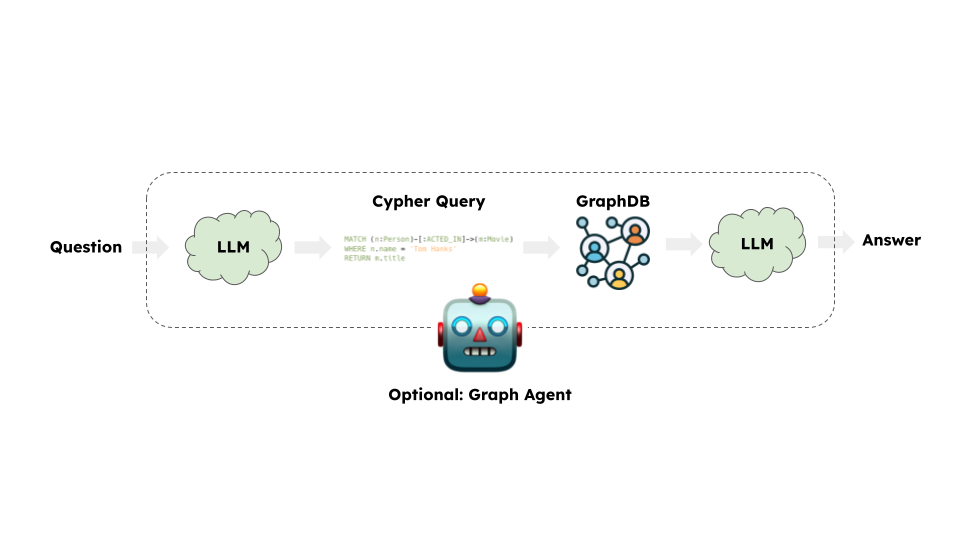
At a high-level, the steps of most graph chains are:
- Convert question to a graph database query: Model converts user input to a graph database query (e.g. Cypher).
- Execute graph database query: Execute the graph database query.
- Answer the question: Model responds to user input using the query results.
Setup
Install dependencies
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm i langchain @langchain/community @langchain/openai @langchain/core neo4j-driver
yarn add langchain @langchain/community @langchain/openai @langchain/core neo4j-driver
pnpm add langchain @langchain/community @langchain/openai @langchain/core neo4j-driver
Set environment variables
We’ll use OpenAI in this example:
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-api-key
# Optional, use LangSmith for best-in-class observability
LANGSMITH_API_KEY=your-api-key
LANGSMITH_TRACING=true
# Reduce tracing latency if you are not in a serverless environment
# LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=true
Next, we need to define Neo4j credentials. Follow these installation steps to set up a Neo4j database.
NEO4J_URI="bolt://localhost:7687"
NEO4J_USERNAME="neo4j"
NEO4J_PASSWORD="password"
The below example will create a connection with a Neo4j database and will populate it with example data about movies and their actors.
import "neo4j-driver";
import { Neo4jGraph } from "@langchain/community/graphs/neo4j_graph";
const url = process.env.NEO4J_URI;
const username = process.env.NEO4J_USERNAME;
const password = process.env.NEO4J_PASSWORD;
const graph = await Neo4jGraph.initialize({ url, username, password });
// Import movie information
const moviesQuery = `LOAD CSV WITH HEADERS FROM
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tomasonjo/blog-datasets/main/movies/movies_small.csv'
AS row
MERGE (m:Movie {id:row.movieId})
SET m.released = date(row.released),
m.title = row.title,
m.imdbRating = toFloat(row.imdbRating)
FOREACH (director in split(row.director, '|') |
MERGE (p:Person {name:trim(director)})
MERGE (p)-[:DIRECTED]->(m))
FOREACH (actor in split(row.actors, '|') |
MERGE (p:Person {name:trim(actor)})
MERGE (p)-[:ACTED_IN]->(m))
FOREACH (genre in split(row.genres, '|') |
MERGE (g:Genre {name:trim(genre)})
MERGE (m)-[:IN_GENRE]->(g))`;
await graph.query(moviesQuery);
Schema refreshed successfully.
[]
Graph schema
In order for an LLM to be able to generate a Cypher statement, it needs
information about the graph schema. When you instantiate a graph object,
it retrieves the information about the graph schema. If you later make
any changes to the graph, you can run the refreshSchema method to
refresh the schema information.
await graph.refreshSchema();
console.log(graph.getSchema());
Node properties are the following:
Movie {imdbRating: FLOAT, id: STRING, released: DATE, title: STRING}, Person {name: STRING}, Genre {name: STRING}
Relationship properties are the following:
The relationships are the following:
(:Movie)-[:IN_GENRE]->(:Genre), (:Person)-[:DIRECTED]->(:Movie), (:Person)-[:ACTED_IN]->(:Movie)
Great! We’ve got a graph database that we can query. Now let’s try hooking it up to an LLM.
Chain
Let’s use a simple chain that takes a question, turns it into a Cypher query, executes the query, and uses the result to answer the original question.

LangChain comes with a built-in chain for this workflow that is designed
to work with Neo4j: GraphCypherQAChain.
The GraphCypherQAChain used in this guide will execute Cypher statements against the provided database.
For production, make sure that the database connection uses credentials that are narrowly-scoped to only include necessary permissions.
Failure to do so may result in data corruption or loss, since the calling code may attempt commands that would result in deletion, mutation of data if appropriately prompted or reading sensitive data if such data is present in the database.
import { GraphCypherQAChain } from "langchain/chains/graph_qa/cypher";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
const llm = new ChatOpenAI({ model: "gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature: 0 });
const chain = GraphCypherQAChain.fromLLM({
llm,
graph,
});
const response = await chain.invoke({
query: "What was the cast of the Casino?",
});
console.log(response);
{ result: "James Woods, Joe Pesci, Robert De Niro, Sharon Stone" }
Next steps
For more complex query-generation, we may want to create few-shot prompts or add query-checking steps. For advanced techniques like this and more check out:
- Prompting strategies: Advanced prompt engineering techniques.
- Mapping values: Techniques for mapping values from questions to database.
- Semantic layer: Techniques for working implementing semantic layers.
- Constructing graphs: Techniques for constructing knowledge graphs.